Pseudo Class Selectors
- Introduction to pseudo-class selectors
- The syntax of pseudo-class selectors
- Link-based pseudo-classes selectrs
- Input and link-based pseudo-class selectors
- Position/number related pseudo-class selectors
- Relational pseudo-class selectors
Introduction to Pseudo Class Selectors
Pseudo-class selectors are used to design special states of the elements, those are not available in the document tree and can't be targeted by the regular CSS selectors.
As you know that any document tree of HTML document is created automatically by the web browser. This document tree is made up of all HTML elements defined by the developer in that HTML document which can be easily accessed and designed by CSS.
But sometimes there are some conditions and states about which there is no information in the document tree. Pseudo-classes are used to target these conditions and states.
For example, when you hover the mouse on the paragraph and you want to change the color of paragraph in red, you can not do this by normal CSS selectors because it is a special state created by a user and there is no information related to it in the document tree.
Similarly, if you just want to make only the first paragraph text color blue of a document, then such conditions can't be targeted by normal CSS selectors. Although it will be in the paragraph document tree however there is no selector available to target it.
Pseudo-classes have been introduced in CSS to design many more similar types of other important states. The details will be explained further. But let's try to know the syntax of pseudo-class selectors before that.
Syntax of Pseudo Class Selectors
The general syntax for pseudo-classes CSS selector has been given below.
selector: pseudo-class
{
property-name: value;
}
You should always keep an eye on the syntax of CSS pseudo. Pseudo-classes always start with a colon (:). Let's now try to find out about the different pseudo-classes available in CSS.
There are a different type of Pseudo Class CSS selectors such as link-based, input & link based, position or number-related, and relational. All Pseudo-class selectors available in CSS are explained with the following example.
There are a different type of Pseudo Class CSS selectors such as link-based, input & link based, position or number-related, and relational. All Pseudo-class selectors available in CSS are explained with the following example.
Link-based pseudo-class selectors
:link - This anchor pseudo-class selector only targets those anchor tags <a> in which the href attribute is defined. The remaining anchor tags are skipped. This class is useful in many important cases. This has been explained by the example below.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
a:link
{
color: red;
text-decoration: none;
background: #ccc;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<br>
<a href="url-will-be-here"> href link1 </a><br><br>
<a> There is no href Link </a><br><br>
<a href="url-will-be-here"> href link2 </a><br><br>
<a> There is no href Link </a><br><br>
<a href="url-will-be-here"> href link3 </a><br><br>
<a> There is no href Link </a>
a:link
{
color: red;
text-decoration: none;
background: #ccc;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<br>
<a href="url-will-be-here"> href link1 </a><br><br>
<a> There is no href Link </a><br><br>
<a href="url-will-be-here"> href link2 </a><br><br>
<a> There is no href Link </a><br><br>
<a href="url-will-be-here"> href link3 </a><br><br>
<a> There is no href Link </a>
</body>
</html>
:visited - This pseudo-class selector only targets such links that have been visited. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
a:visited
{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.google.co.in" target="_blank"> GOOGLE </a><br>
<a href="https://www.mybloghelp.com" target="_blank"> My Blog Help </a><br>
<a href="https://www.yahoo.com" target="_blank"> YAHOO </a>
</body>
a:visited
{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.google.co.in" target="_blank"> GOOGLE </a><br>
<a href="https://www.mybloghelp.com" target="_blank"> My Blog Help </a><br>
<a href="https://www.yahoo.com" target="_blank"> YAHOO </a>
</body>
</body>
</html>
:hover - When the cursor of the mouse is moved to an element, that element moves into the hover state. This pseudo-class selector is used to target the same hover state. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p{
width: 30%;
text-align: justify;
}
p:hover
{
color: hotpink;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 25px;
background: lightgray;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the paragraph Where you will bring your mouse on the paragraph, its text color will be hotpink, font weight will be bolder, font size will be 25px, and background will be lightgray. </p>
p{
width: 30%;
text-align: justify;
}
p:hover
{
color: hotpink;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 25px;
background: lightgray;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the paragraph Where you will bring your mouse on the paragraph, its text color will be hotpink, font weight will be bolder, font size will be 25px, and background will be lightgray. </p>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:active - This class selector is used to target the pressed(clicked) state of a link or button. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
a:active
{
color: hotpink;
background: lightgray;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 25px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> Below link color turns hotpink during its pressed state </p>
<a href="https://www.mybloghelp.com"> MyBlogHelp </a>
a:active
{
color: hotpink;
background: lightgray;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 25px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> Below link color turns hotpink during its pressed state </p>
<a href="https://www.mybloghelp.com"> MyBlogHelp </a>
</body>
</html>
Input and link-based pseudo-class selectors
:focus - When an element comes into focus then this pseudo-class CSS selector is used to target that state. This class mainly targets the same elements that take input through the keyboard. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:focus
{
background-color: lightblue;
color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "First_Name"> <br/> <br/>
Last Name: <input type = "text" name = "Last_Name"> <br/> <br/>
User Name: <input type = "text" name = "User_Name"> <br/> <br/>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email_Id"> <br/> <br/>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
input:focus
{
background-color: lightblue;
color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "First_Name"> <br/> <br/>
Last Name: <input type = "text" name = "Last_Name"> <br/> <br/>
User Name: <input type = "text" name = "User_Name"> <br/> <br/>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email_Id"> <br/> <br/>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:target - This class selector is used to apply CSS rules to target elements. When you do not enter the URL in a link, you pass the ID of another element with the # symbol, then clicking on that link, focus move on that element. In this situation, the second element is the target element, which is used to design this class. This class has been explained by the example below.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
:target
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#Paragraph1"> Go to first Paragraph </a><br>
<a href="#Paragraph2"> Go to second Paragraph </a><br>
<a href="#Paragraph3"> Go to third Paragraph </a>
<p>Click on the above link which paragraph you want to read.</p>
<p id="Paragraph1"> This is the first paragraph. </p>
<p id="Paragraph2"> This is the second paragraph. </p>
<p id="Paragraph3"> This is the third paragraph. </p>
:target
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#Paragraph1"> Go to first Paragraph </a><br>
<a href="#Paragraph2"> Go to second Paragraph </a><br>
<a href="#Paragraph3"> Go to third Paragraph </a>
<p>Click on the above link which paragraph you want to read.</p>
<p id="Paragraph1"> This is the first paragraph. </p>
<p id="Paragraph2"> This is the second paragraph. </p>
<p id="Paragraph3"> This is the third paragraph. </p>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:enabled - This CSS class selector selects such input elements which are enabled by default which can be used. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:enabled
{
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "First_Name" > <br><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" name="Last_Name"> <br><br>
User Name: <input type="text" name="User_Name" disabled> <br><br>
Email: <input type = "email" name = "Email_Id"> <br><br>
Tel: <input type = "number" name = "Tel_Num" disabled> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
input:enabled
{
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "First_Name" > <br><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" name="Last_Name"> <br><br>
User Name: <input type="text" name="User_Name" disabled> <br><br>
Email: <input type = "email" name = "Email_Id"> <br><br>
Tel: <input type = "number" name = "Tel_Num" disabled> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:disabled - This pseudo-class CSS selector targets such elements that are disabled. It is mainly used with form elements. It has been explained through an example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:disabled
{
background: hotpink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "First_Name" > <br><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" name="Last_Name"> <br><br>
User Name: <input type="text" name="UserName" disabled> <br><br>
Email: <input type = "email" name = "Email_Id"> <br><br>
Tel: <input type = "number" name = "Tel_Num" disabled> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
input:disabled
{
background: hotpink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "First_Name" > <br><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" name="Last_Name"> <br><br>
User Name: <input type="text" name="UserName" disabled> <br><br>
Email: <input type = "email" name = "Email_Id"> <br><br>
Tel: <input type = "number" name = "Tel_Num" disabled> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
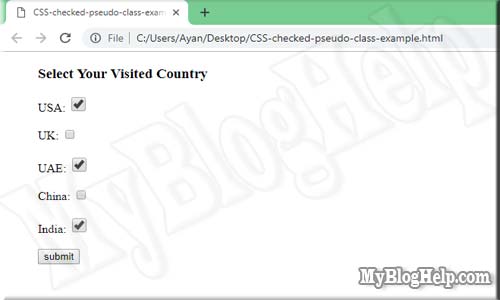
:checked - This pseudo-class CSS selector is used to target such checkboxes that have been checked. For example, suppose you want to increase the height and width of the checkbox when you check so you can use this class for it. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:checked
{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<h3>Select Your Visited Country</h3>
<form>
USA: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Usa"> <br><br>
UK: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Uk"> <br><br>
UAE: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Uae"> <br><br>
China: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Chn"> <br><br>
India: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Ind"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
</form>
input:checked
{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<h3>Select Your Visited Country</h3>
<form>
USA: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Usa"> <br><br>
UK: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Uk"> <br><br>
UAE: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Uae"> <br><br>
China: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Chn"> <br><br>
India: <input type = "checkbox" name = "Ind"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
</form>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:indeterminate - This pseudo-class is used to target such a form element whose state is indeterminate.
:valid - This pseudo-class selector targets such form elements for which validation is performed and where the user inputs valid value. For example, by this class, you can display the background color light blue of the text box when the user inputs a valid email address in the email input type. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:valid
{
background-color: lightblue;
color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Login Your Account </h1>
<form>
Username: <input type = "text" name = "Uname"> <br><br>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email"> <br><br>
Password: <input type = "password" name = "Pwd"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
input:valid
{
background-color: lightblue;
color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Login Your Account </h1>
<form>
Username: <input type = "text" name = "Uname"> <br><br>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email"> <br><br>
Password: <input type = "password" name = "Pwd"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, when the user will enter valid email address input, the background color of the text box will be light blue and if the email address format is not valid then the text box background color will be white.
This example will produce the below output.
:invalid - This pseudo-class CSS selector targets such form elements for which validation is performed and in which input an invalid value. For example, by this class, you can show background color red when you input an invalid email address in the email input type. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:invalid
{
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Login Your Account </h1>
<form>
Username: <input type = "text" name = "Uname"> <br><br>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email"> <br><br>
Password: <input type = "password" name = "Pwd"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
input:invalid
{
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Login Your Account </h1>
<form>
Username: <input type = "text" name = "Uname"> <br><br>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email"> <br><br>
Password: <input type = "password" name = "Pwd"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:required - This pseudo-class selector targets such form elements for which the required attribute has been defined. Required means, the input field is mandatory you can't leave it blank. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:required
{
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Enter you Email Id below </h1>
<form>
Username: <input type = "text" name = "Uname"> <br><br>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email" required> <br><br>
Password: <input type = "password" name = "Pwd" required> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
input:required
{
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Enter you Email Id below </h1>
<form>
Username: <input type = "text" name = "Uname"> <br><br>
Email Id: <input type = "email" name = "Email" required> <br><br>
Password: <input type = "password" name = "Pwd" required> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
:optional - This pseudo-class CSS selector targets such form elements for which the required attribute has not been defined. Optional means, the input field is not mandatory you can leave it blank. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:optional
{
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
User Name: <input type = "text" name = "uName"> <br/> <br/>
Email: <input type = "email" name = "Email" required> <br/> <br/>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
input:optional
{
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
User Name: <input type = "text" name = "uName"> <br/> <br/>
Email: <input type = "email" name = "Email" required> <br/> <br/>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
:out-of-range - This pseudo-class selector targets such form elements whose value is inputted out of the range. But it will work only for input elements in which the range is defined by min and max attributes. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
margin-left: 50px;
}
input:out-of-range
{
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<h2> Enter a number between 10 to 20 </h2>
<input type = "number" min = "10" max = "20"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
body
{
margin-left: 50px;
}
input:out-of-range
{
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<h2> Enter a number between 10 to 20 </h2>
<input type = "number" min = "10" max = "20"> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:readonly - This pseudo-class CSS selector targets such input elements for which readonly attribute has been defined. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input:read-only
{
background-color: blue;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
Name: <input type = "text" name = "Name"> <br><br>
Country: <input type = "text" value = "USA" readonly> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
input:read-only
{
background-color: blue;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
Name: <input type = "text" name = "Name"> <br><br>
Country: <input type = "text" value = "USA" readonly> <br><br>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
:readwrite - This pseudo-class targets such input elements for which readonly attribute has not been defined.
Position/number-based pseudo-class selectors
:root - This selector is used to target the root element of the document. The root element is always the <html> element in an HTML document. This has been explained by the example below.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
:root
{
background-color: green;
color: red;
font-size: 25px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> My Blog Help </h1>
:root
{
background-color: green;
color: red;
font-size: 25px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> My Blog Help </h1>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:first-child - This class targets the specified selector but only when it is the first child of its parent. For example, if you want to make the background color light gray and text color blue of all the paragraphs in the document which is the first child of its parent then you can use this pseudo-class for it. This is understood by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p
{
width: 500px;
}
p:first-child
{
background-color: lightgray;
color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent body. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent body. </p>
<header>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent header. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent header. </p>
</header>
<div>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent div. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent div. </p>
</div>
<footer>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent footer. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent footer. </p>
</footer>
p
{
width: 500px;
}
p:first-child
{
background-color: lightgray;
color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent body. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent body. </p>
<header>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent header. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent header. </p>
</header>
<div>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent div. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent div. </p>
</div>
<footer>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent footer. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent footer. </p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
The above example produces the below output.
:last-child - This class targets the specified selector but only when it is the last child of its parent. For example, if you want to target all the paragraphs those are the last child of the parent element then in that situation, you can use this class. This has been explained by the example below.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
width: 600px;
}
p:last-child
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the first child of its parent header. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent header. </p>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the LAST child of its parent header. </p>
</header>
<div>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent div. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent div. </p>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the LAST child of its parent div. </p>
</div>
<footer>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent footer. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent footer. </p>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the LAST child of its parent footer. </p>
</footer>
body
{
width: 600px;
}
p:last-child
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the first child of its parent header. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent header. </p>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the LAST child of its parent header. </p>
</header>
<div>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent div. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent div. </p>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the LAST child of its parent div. </p>
</div>
<footer>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the first child of its parent footer. </p>
<p> This paragraph will not be targeted because it is the second child of its parent footer. </p>
<p> This paragraph will be targeted because it is the LAST child of its parent footer. </p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
:nth-child () - This is the pseudo-class selector by which you can target the child element of any number. For example, if you want to target every paragraph that is the third child of the parent then you can use this pseudo-class.
This class manages the same order of all types of elements. So if there is no third child paragraph of an element, then no element will be targeted.
A number or expression argument is passed in this pseudo-class. As if you want to target the third child element, you will pass 3. It does not matter what type of parent is. It has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p:nth-child(4)
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the first child of div </p>
<span> This is the second child of div </span>
<h4> This is the third child of div </h4>
<p> This is the fourth child of div </p>
<p> This is the fifth child of div </p>
</div>
p:nth-child(4)
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the first child of div </p>
<span> This is the second child of div </span>
<h4> This is the third child of div </h4>
<p> This is the fourth child of div </p>
<p> This is the fifth child of div </p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:nth-of-type () - This pseudo-class CSS selector targets a particular type of child element. For example, you want to target only every second child element of a particular type (p, span, etc.).
For this, you can use this pseudo-class. This class is helpful in situations where there are a lot of elements within the parent element and you want to target only a particular type element.
This class manages different order of every type of child elements. So, the child element, with a specific position from all the child elements of that type, is targeted. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
span:nth-of-type(3)
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span> This is the first span of body. </span>
<p> This is the first paragraph of body. </p>
<span> This is the second span of body. </span>
<p> This is the second paragraph of body. </p>
<span> This is the third span of body. </span>
<p> This is the third paragraph of body. </p>
span:nth-of-type(3)
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span> This is the first span of body. </span>
<p> This is the first paragraph of body. </p>
<span> This is the second span of body. </span>
<p> This is the second paragraph of body. </p>
<span> This is the third span of body. </span>
<p> This is the third paragraph of body. </p>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:first-of-type - This pseudo-class selector targets an element of a particular type that is the first child element of its parent element. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
span:first-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the first paragraph </p>
<span> This is the first span will be targeted </span>
<p> This is the second paragraph </p>
<span> This is the second span which will not be targeted </span>
</div>
span:first-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the first paragraph </p>
<span> This is the first span will be targeted </span>
<p> This is the second paragraph </p>
<span> This is the second span which will not be targeted </span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:last-of-type - This pseudo-class selector targets an element of a particular type that is the last child element of its parent element. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
width: 500px;
}
p:last-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
span:last-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the first paragraph type of div which will not be targeted. </p>
<span> This is the first span type of div which will not be targeted. </span>
<p> This is the Last paragraph type of div which will be targeted. </p>
<span> This is the Last span type of div which will be targeted. </span>
</div>
body
{
width: 500px;
}
p:last-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
span:last-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the first paragraph type of div which will not be targeted. </p>
<span> This is the first span type of div which will not be targeted. </span>
<p> This is the Last paragraph type of div which will be targeted. </p>
<span> This is the Last span type of div which will be targeted. </span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:nth-last-of-type () - This pseudo-class works as nth-of-type () but its counting is done from the bottom side. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
width: 30%;
margin-left: 50px;
}
p:nth-last-of-type(1)
{
color: blue;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
span:nth-last-of-type(2)
{
color: blue;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the First Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Second Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Third Paragraph </p>
<p> This is the Fourth Paragraph wich will be targeted. </p>
<span> This is the First Span. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Second Span. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Third Span. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Fourth Span which will be targeted. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Fifth Span. </span>
</div>
body
{
width: 30%;
margin-left: 50px;
}
p:nth-last-of-type(1)
{
color: blue;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
span:nth-last-of-type(2)
{
color: blue;
background-color: hotpink;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is the First Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Second Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Third Paragraph </p>
<p> This is the Fourth Paragraph wich will be targeted. </p>
<span> This is the First Span. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Second Span. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Third Span. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Fourth Span which will be targeted. </span> <br>
<span> This is the Fifth Span. </span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:nth-last-child () - This works like pseudo class nth-child but its counting is done from the bottom side. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
width: 35%;
margin-left: 50px;
}
:nth-last-child(4)
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the First Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Second Paragraph which will be targeted. </p>
<p> This is the Third Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Fourth Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Fifth Paragraph. </p>
body
{
width: 35%;
margin-left: 50px;
}
:nth-last-child(4)
{
color: red;
background-color: lightgray;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the First Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Second Paragraph which will be targeted. </p>
<p> This is the Third Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Fourth Paragraph. </p>
<p> This is the Fifth Paragraph. </p>
</body>
</html>
:only-of-type - This CSS pseudo-class selector targets an element that has the only one child element of a parent element in its own particular type. There should not be siblings of the same type. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
width: 35%;
margin-left: 50px;
}
p:only-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: hotpink;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<p> This Paragraph is the child of header. </p>
<p>This paragraph is sibling of header</p>
</header>
<div>
<p> This is only one child Paragraph of Div. There is no siblings. </p>
</div>
<footer>
<p> This Paragraph is the child of footer. </p>
<p>This paragraph is sibling of footer</p>
<p>This paragraph is sibling of footer</p>
</footer>
body
{
width: 35%;
margin-left: 50px;
}
p:only-of-type
{
color: blue;
background-color: hotpink;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<p> This Paragraph is the child of header. </p>
<p>This paragraph is sibling of header</p>
</header>
<div>
<p> This is only one child Paragraph of Div. There is no siblings. </p>
</div>
<footer>
<p> This Paragraph is the child of footer. </p>
<p>This paragraph is sibling of footer</p>
<p>This paragraph is sibling of footer</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
:only-child - This pseudo-class selector targets such element that is the only one child of the parent element. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p:only-child
{
color: blue;
background: lightgray;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is First child of Div1 </p>
<p> This is Second child of Div1 </p>
</div>
<div>
<p> This is only one child of Div2 </p>
</div>
<div>
<p> This is First child of Div3 </p>
<p> This is Second child of Div3 </p>
</div>
p:only-child
{
color: blue;
background: lightgray;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p> This is First child of Div1 </p>
<p> This is Second child of Div1 </p>
</div>
<div>
<p> This is only one child of Div2 </p>
</div>
<div>
<p> This is First child of Div3 </p>
<p> This is Second child of Div3 </p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.
Relational pseudo-class selectors
:not() - This selector applies to the other elements except for the specified class. For example, you want to make the text color red of all elements, except for a specific element such as span, then you can use this pseudo-class.
Apart from this, if you are targeting elements of the same type but you want to exclude any particular element from CSS rule, you can pass the ID of that particular element in this pseudo-class. This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
width: 30%;
}
p:not(#mbhPara)
{
color: blue;
background: yellow;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the first paragraph which is selected </p>
<p id="mbhPara"> This is second paragraph which is not selected </p>
<p > This is the third paragraph which is selected </p>
<p id="mbhPara"> This is the fourth paragraph which is not selected </p>
<p> This is the fifth paragraph which is selected </p>
body
{
width: 30%;
}
p:not(#mbhPara)
{
color: blue;
background: yellow;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the first paragraph which is selected </p>
<p id="mbhPara"> This is second paragraph which is not selected </p>
<p > This is the third paragraph which is selected </p>
<p id="mbhPara"> This is the fourth paragraph which is not selected </p>
<p> This is the fifth paragraph which is selected </p>
</body>
</html>
:empty - This selector is used to target such elements in which no content is defined and also there are no child elements. Such elements are called empty elements. It has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p:empty
{
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
background: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the First Paragraph and below paragraph is empty because there is no content. </p> <br>
<p> </p> <br>
<p> This is another paragraph. </p>
p:empty
{
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
background: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p> This is the First Paragraph and below paragraph is empty because there is no content. </p> <br>
<p> </p> <br>
<p> This is another paragraph. </p>
</body>
</html>
As you can see in the above example, the background color of the empty element will be displayed only when you define its width and height because there is no content in the empty elements, so they do not have any width and height. This example will produce the below output.
: lang - This class is used to select such elements in which the lang attribute define with the specified value. For example, you just want to target those elements in which the value of lang attribute is defined en (English). This has been explained by the below example.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p:lang(en)
{
color: blue;
background: yellow;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p lang="en-us"> Language is defined in US English. </p>
p:lang(en)
{
color: blue;
background: yellow;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p lang="en-us"> Language is defined in US English. </p>
</body>
</html>
The above example will produce the below output.



































0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Thank you for reading this post. Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.